DBS (Deep Brain Stimuation)
Deep Brain Stimuation
Deep brain stimulation (DBS) is a surgical procedure that involves implanting a medical device, called a neurostimulator, into the brain. This device delivers electrical stimulation to specific areas of the brain, which can help to treat a variety of neurological disorders.
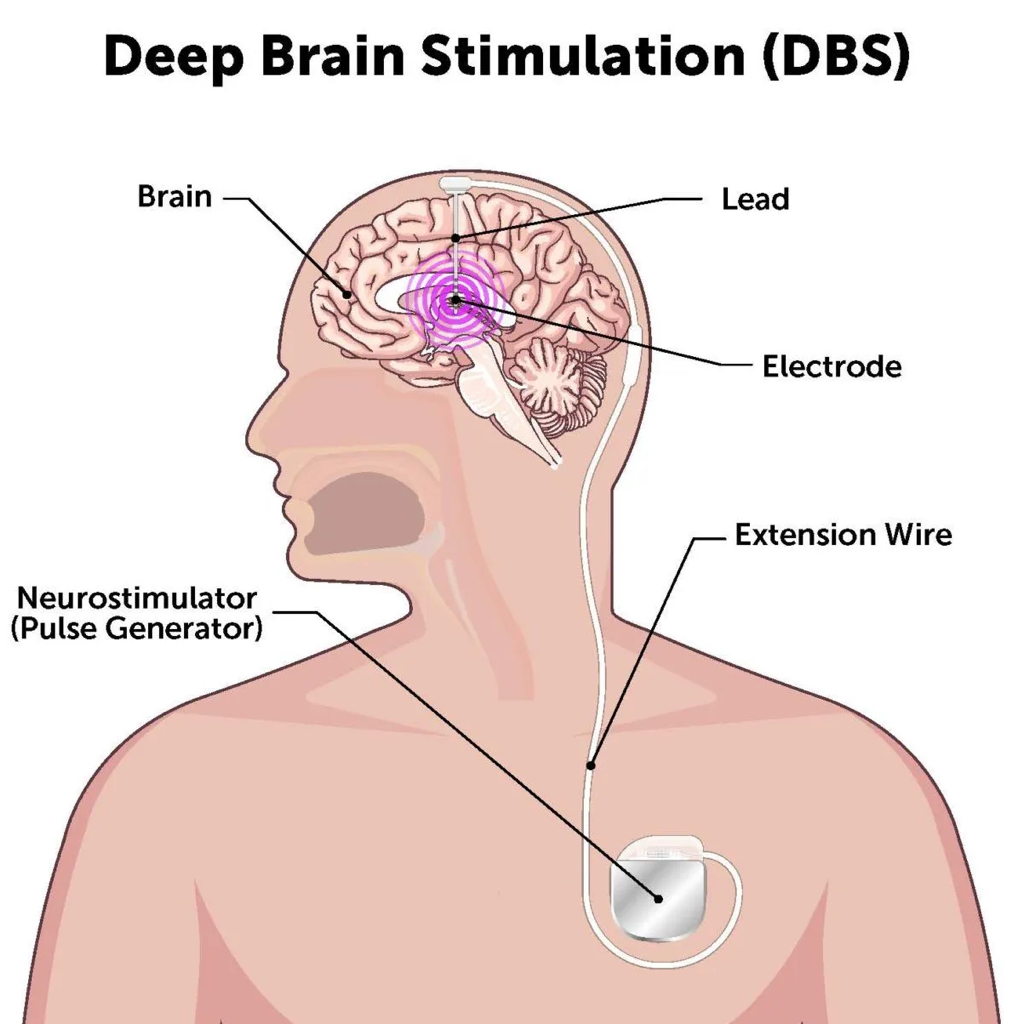
It’s important to note that DBS is not a cure for any neurological disorder. The treatment is most effective when used in conjunction with other therapies, such as medication. If you are considering DBS, it is important to discuss the risks and benefits with your doctor.
Types of DBS
Deep brain stimulation (DBS) can target different areas of the brain, depending on the specific neurological disorder being treated. Here are some of the most common targets:
For movement disorders:
- Subthalamic nucleus (STN): This is a common target for Parkinson’s disease, as it helps to regulate movement.
- Globus pallidus internus (GPi): This is another target for Parkinson’s disease, as well as essential tremor and dystonia.
For other conditions:
- Thalamus: This is a target for chronic pain and epilepsy.
It’s important to note that these are just a few examples, and DBS can target other areas of the brain depending on the specific needs of the patient. The decision of which area to target is made by the neurosurgeon based on the patient’s diagnosis, symptoms, and overall health.
Alternatives to Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS)
While DBS is a powerful tool for treating certain neurological disorders, it’s not always the most suitable option for everyone. Here are some alternatives to consider:
Medical Management
- Medications: For conditions like Parkinson’s disease, essential tremor, and dystonia, medications can often effectively manage symptoms
- Physical therapy: This can help improve mobility and reduce pain in conditions like Parkinson’s disease and dystonia.
- Occupational therapy: This can assist individuals in adapting to their condition and maintaining daily activities.
Surgical Interventions (Non-DBS)
- Stereotactic radiosurgery: This non-invasive procedure uses focused radiation beams to target abnormal brain tissue. It can be considered for conditions like essential tremor and trigeminal neuralgia.
- Lesioning: This involves surgically destroying a specific area of the brain. It’s less commonly used today due to the potential for significant side effects.
Lifestyle Modifications
- Diet and exercise: A healthy lifestyle can help manage symptoms of certain neurological disorders.
- Stress management: Techniques like meditation and yoga can help reduce stress and improve overall well-being.
- Support groups: Connecting with others who have similar experiences can provide emotional support and practical advice.
It’s crucial to consult with a healthcare professional to discuss the most appropriate treatment options based on your individual circumstances. They can evaluate your condition, weigh the risks and benefits of different approaches, and recommend the best course of action.
Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS) is primarily beneficial for individuals with certain neurological disorders. It can be an effective treatment option for people who:
Have Parkinson’s disease: DBS can help manage symptoms like tremors, rigidity, and slowness of movement.
Experience essential tremor: This condition causes involuntary shaking, and DBS can reduce its severity.
Suffer from dystonia: A neurological disorder characterized by muscle spasms and contractions, DBS can improve symptoms.
Have obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD): For individuals with severe, treatment-resistant OCD, DBS can help reduce intrusive thoughts and compulsive behaviors.
Experience chronic pain: In some cases, DBS can be used to manage chronic pain that is not relieved by other treatments.
It’s important to note that DBS is not a cure for these conditions. Rather, it is a treatment option that can help improve symptoms and quality of life for many individuals.
If you or someone you know is considering DBS, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare professional. They can evaluate your condition, discuss the potential benefits and risks, and determine if DBS is a suitable option.
Have obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD): For individuals with severe, treatment-resistant OCD, DBS can help reduce intrusive thoughts and compulsive behaviors.
Experience chronic pain: In some cases, DBS can be used to manage chronic pain that is not relieved by other treatments.
It’s important to note that DBS is not a cure for these conditions. Rather, it is a treatment option that can help improve symptoms and quality of life for many individuals.
If you or someone you know is considering DBS, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare professional. They can evaluate your condition, discuss the potential benefits and risks, and determine if DBS is a suitable option.
Who is Not Suitable for DBS?
While DBS can be a life-changing treatment for many people, it is not suitable for everyone. Some factors that may make a person ineligible for DBS include:
Severe medical conditions: Individuals with severe heart, lung, or other systemic diseases may not be candidates for DBS.
Cognitive impairment: People with severe cognitive impairment or dementia may not be suitable for DBS.
Substance abuse: Active substance abuse can make DBS less effective and increase the risk of complications.
Lack of informed consent: Individuals must be able to understand the risks and benefits of DBS and provide informed consent for the procedure.
It’s essential to consult with a healthcare professional to determine if DBS is a suitable option for you. They can evaluate your condition, discuss the potential benefits and risks, and provide personalized guidance.
